Digital System & Digital Design
What is System?
Machine: A machine is a tool containing one or more parts that uses energy to perform an intended action.
-
Machines are usually powered by mechanical, chemical, thermal, or electrical means, and are often motorized.
-
Historically, a power tool also required moving parts to classify as a machine.
System:
-
A set of detailed methods, procedures and routines created to carry out a specific activity, perform a duty, or solve a problem.
-
An organized, purposeful structure that consists of interrelated and interdependent elements (components, entities, factors, members, parts etc.).
-
These elements continually influence one another (directly or indirectly) to maintain their activity and the existence of the system, in order to achieve the goal of the system.
System Classification
System can be classified in so many ways:
-
Type of Energy used: Mechanical, Electrical, Electronics, etc…
-
Size: Mega, mini, Micro
-
Liner and Non-liner Systems
-
Time Variant and Time Invariant Systems
-
Liner Time variant and Liner Time invariant systems
-
Static and Dynamic Systems
-
Causal and Non-causal Systems
-
Invertible and Non-Invertible Systems
-
Stable and Unstable Systems
-
Analog and Digital Systems
Control System
Open loop
Closed loop: Feedback
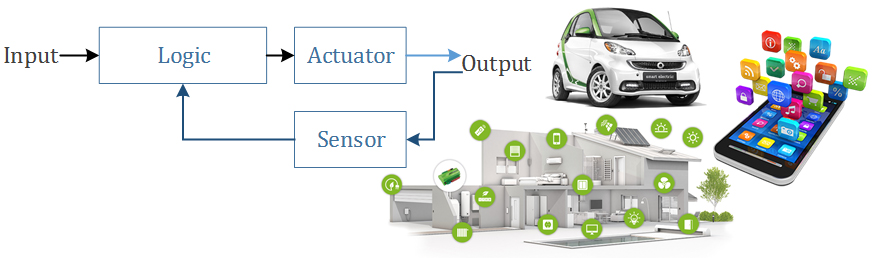
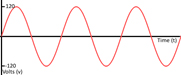
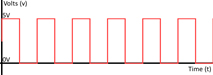
Analog Vs Digital System
Open loop
|
Analog |
Digital |
|---|---|---|
Signal |
Analog signal is a continuous signal which represents physical measurements. | Digital signals are discrete time signals generated by digital modulation. |
Waves |
Denoted by sine waves |
Denoted by square waves |
Representation |
Uses continuous range of values to represent information |
Uses discrete or discontinuous values to represent information |
Technology |
Analog technology records waveforms as they are. |
Samples analog waveforms into a limited set of numbers and records them. |
Data transmissions |
Subjected to deterioration by noise during transmission and write/read cycle. |
Can be noise-immune without deterioration during transmission and write/read cycle. |
Response to Noise |
More likely to get affected reducing accuracy |
Less affected since noise response are analog in nature |
Flexibility |
Analog hardware is not flexible. |
Digital hardware is flexible in implementation. |
Uses |
Can be used in analog devices only. Best suited for audio and video transmission. |
Best suited for Computing and digital electronics. |
Applications |
Thermometer |
PCs, PDAs |
Bandwidth |
Analog signal processing can be done in real time and consumes less bandwidth. |
There is no guarantee that digital signal processing can be done in real time and consumes more bandwidth to carry out the same information. |
Memory |
Stored in the form of wave signal |
Stored in the form of binary bit |
Power |
Analog instrument draws large power |
Digital instrument draw only negligible power |
Cost |
Low cost and portable |
Cost is high and not easily portable |
Impedance |
Low |
High order of 100 megaohm |
Errors |
Analog instruments usually have a scale which is cramped at lower end and give considerable observational errors. |
Digital instruments are free from observational errors like parallax and approximation errors. |
Example |
Human voice in air, analog electronic devices. |
Computers, CDs, DVDs, and other digital electronic devices. |
 |
 |
Why Digital?
Advantages of Digital –
|
Disadvantages of Digital – |
| ○ Ease of programmability / manipulate ○ High Speed ○ More reliable ○ Design is easy as its flexible ○ Compatibility with other digital systems ○ Only digitised information can be transported through a noisy channel without degradation ○ Integrated networks ○ Reduction in cost of hardware so less expensive ○ Results can be reproduced easily ○ Information storage can be easier in digital computer systems than in analog ones. |
○ Use more energy than analog circuits to accomplish the same tasks, thus producing more heat as well. |
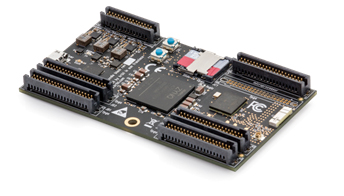
How to design Digital System?
Discrete Chips |
 |
Prototype using FPGA |
 |
Application Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) |
 |
Digital Design Fundamentals
Digital Signals
| ○ Digital Signal is a signal that represents a sequence of discrete values. ○ A logic signal is a digital signal with only two possible values, and describes an arbitrary bit stream. ○ Other types of digital signals can represent three-valued logic or higher valued logics. ○ Digital signals are represented by Binary Number. |
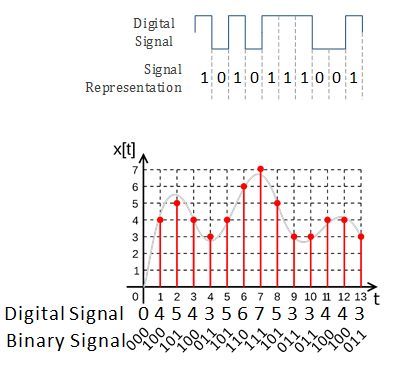 |
Binary Signal
| ○ Binary (or "base-2") a numeric system that only uses two digits — 0 and 1. ○ Computers operate in binary, meaning they store data and perform calculations using only zeros and ones. ○ While a single binary digit can be used to represent True (1) or False (0) in Boolean logic, multiple binary digits can be used to store large numbers and perform complex functions. ○ In fact, any number can be represented in binary. |
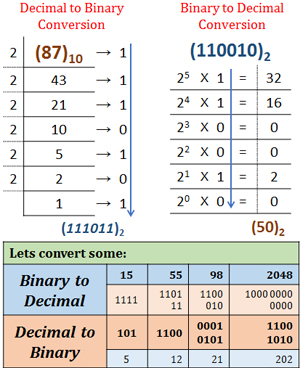 |
Electronics and Switches
○ Electronic switches are the basis of binary digital circuits ○ A switch has three parts ○ CMOS transistor |
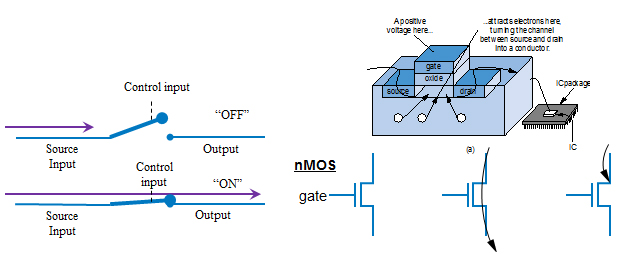 |
Boolean Logic Gates
○ Building Blocks for Digital Circuits |
| ○ "Logic gates" are better digital circuit building blocks than switches (transistors) ●Why?... |
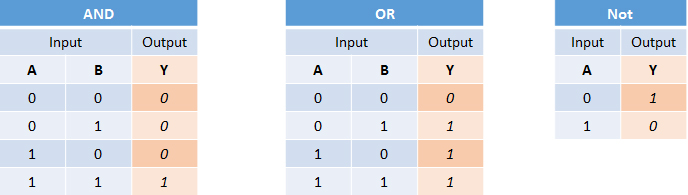
Boolean Algebra & its Relation to Digital Circuits
○ Boolean Algebra |
Converting to Boolean Equations
-
Q1. a is 1 and b is 1.
-
Q2. either of a or b is 1.
-
Q3. both a and b are not 0.
Answer: F = a AND b
Answer: F = a OR b
Answer:
(a) Option 1: F = NOT(a) AND NOT(b)
(b) Option 2: F = a OR b
Relating Boolean Algebra to Digital Design
-
Implement Boolean operators using transistors
Call those implementations logic gates.
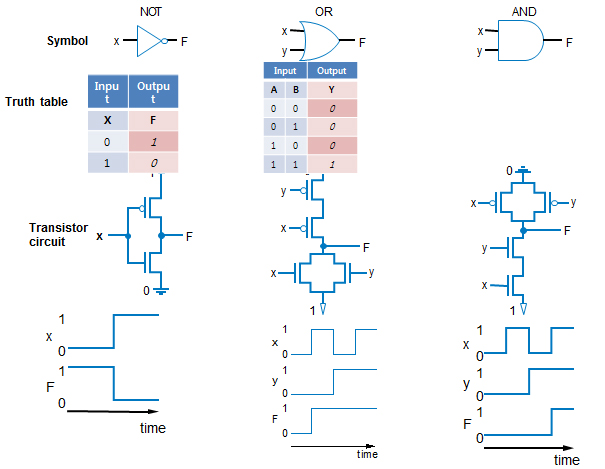
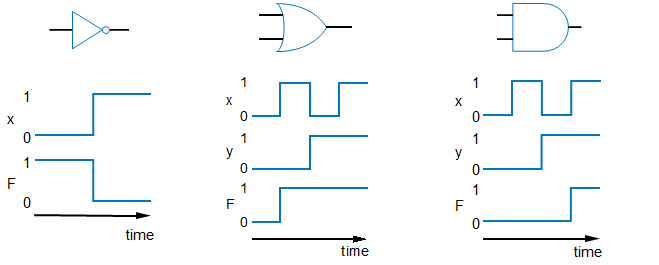
NOT/OR/AND Logic Gate Timing
-
Diagrams